Vocabular y Review
Jumble the Key Words and write them on the board or on chart paper. Then, have
students brainstorm a list of examples based on the words, such as gases and oil
as resources. Ask students to create word jumbles from their examples. Have them
write their jumbles on the board for the class to unscramble.
Practice Tactics
Have students open their Practice Book to page 55. Read the directions aloud
and have students read along with you. Explain the directions and model the activity.
Then, have students complete the page as independent class work or homework.
Home Connection
Write the Key Vocabulary on the board randomly for students to alphabetize.
Distribute Blackline Masters 2a and 2b. If necessary, review with students
how to fold the sheet to create a booklet. Provide more folded sheets if
necessary. Ask students to complete the first page by writing their names,
date, My Dictionary, and subject area. Have them write the words on the
remaining pages in a column. Next, ask students to use their own words to
write definitions for each word. Have them check their work by looking up
the correct definitions in their dictionaries. Explain that they should read their
definitions to their parents or guardians. Remind them to return their booklets
to school. Retain them for future use.
My Community
Unit 4
139
$
"$
$ " #
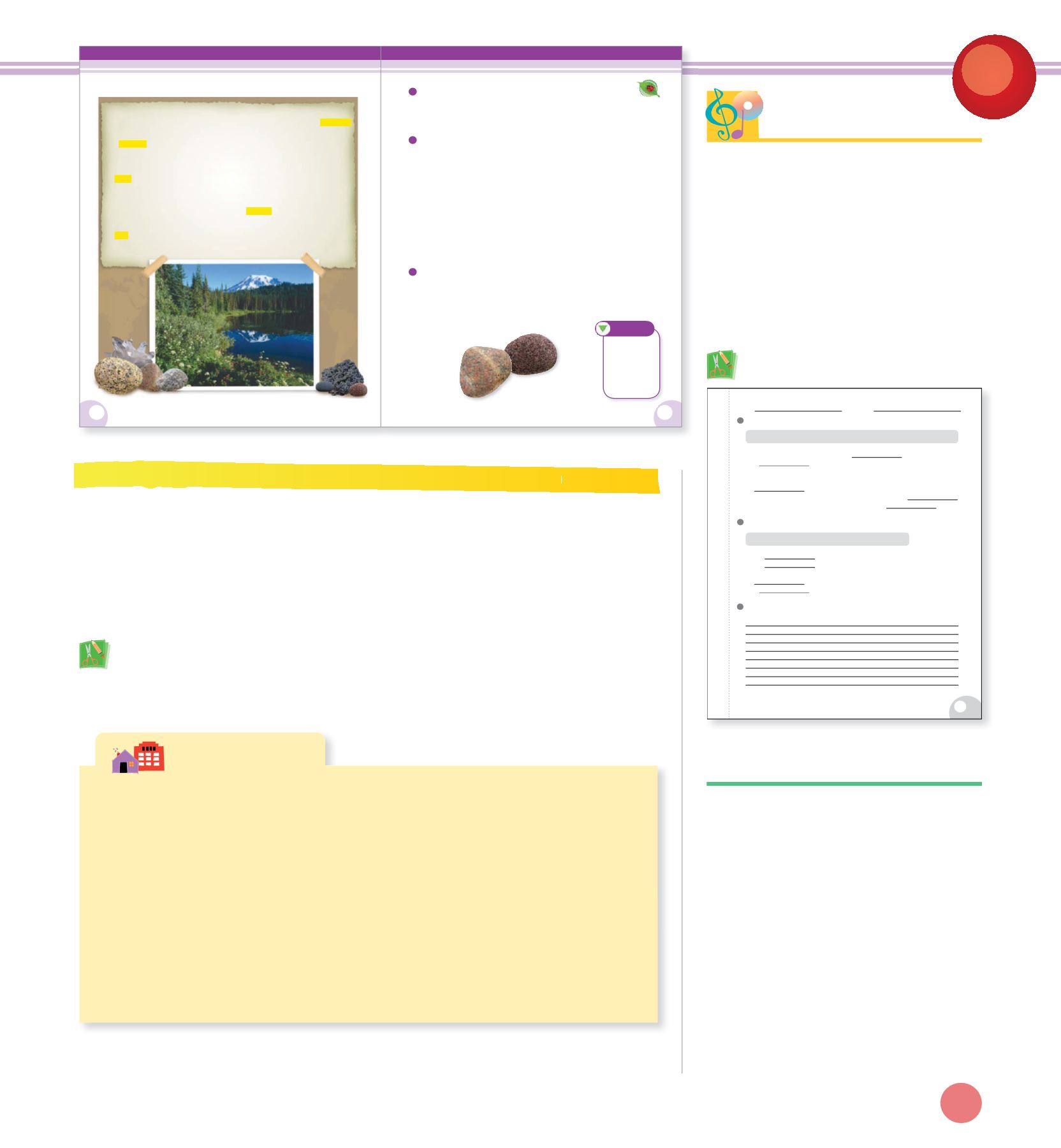
E tar h materi la s are solid ro kc s and il so s w, ta er an, d the gases that make up
the atmo hsp ere. These materials have different physical and chemi lca pert
pro ies
that make them useful in different ways. Earth materials provide many of
the
urce that humans use. For example, rocks can be used as building
reso s
materials; gases and oils found under the ground can be used as sources of
fuel; and soils can be used for growing the plants we use as food.
vary in size, from tiny pebbles to huge mountains. They also vary in
Rocks
shape, color, and texture. Size, shape, color, and texture are known as properties
of rocks. Some rocks are made of a single material, but most are made of
several materials. These substances are called minerals. Minerals are substances
that we find in nature, but are neither plants nor animals.
have properties of color and texture. They can hold water, and they can
Soils
support the growth of many kinds of plants, including those in our food supply.
$
&0* & <&10 &74:3) 9-* 8(-441 51&>,74:3) & 5&70 47 >4:7
3*.,-'47-44) '8*7;* 9-* ,74:3) #-&9 .8 9-* ).++*7*3(* '*9<**3
9-* 897**9 9-* 8.)*<&10 &3) 9-* 84.1 #-&9 &7* 9-*> 2&)* 4+
#-&9 (4147 &7* 9-*>
.3) & 74(0 .3 9-* 8(-441 51&>,74:3) & 5&70
47 >4:7 3*.,-'47-44)
'8*7;* 9-* 74(0 :8.3, &11 4+ >4:7 8*38*8
#-&9 )4*8 .9 +**1 1.0* 8 .9 8-&75 47 82449-
4< -*&;> .8 .9 4*8 .9 +**1 -*&;> 47 1.,-9
#-&9 )4*8 .9 1440 1.0* 4*8 .9 85&701* 47 .8 .9 ):11
8 .9 &11 43* (4147 47 )4*8 .9 -&;* ).++*7*39 (41478
#-&9 )4*8 .9 82*11 1.0* 4*8 .9 -&;* &3 4)47
'8*7;* 9-* 74(0 :8.3, & 2&,3.+>.3, ,1&88 4 >4: 349.(*
&3>9-.3, *18* &'4:9 9-* 74(0 9-&9 >4: ).) 349 8**
'*+47* *8(7.'* <-&9 >4: 4'8*7;*
#7.9* &'4:9 9-* 74(0
*8(7.'* <-*7* >4: +4:3) 9-* 74(0 * 8:7* 94 .3(1:)* )*9&.18
&'4:9 9-* 84.1 >4: +4:3) .9 .3 &3) <-&9 <&8 3*&7 .9
*8(7.'* <-&9 >4: 4'8*7;*) &'4:9 9-* 74(0
*8(7.'* <-*7* >4: 9-.30 9-* 74(0 2.,-9 -&;*
(42* +742
*> #47)8
2.3*7&18
5745*79.*8
7*84:7(*8
74(08
84.18
Freeze!
Tell students that as you play music, they
are to move to it by dancing, marching,
swaying, and so on. As soon as the music
stops, they are to freeze. Students who move
after the music stops should sit down outside
the area where others are still participating.
Play the music on and off until only one
person is left standing.
Multiple Intelligences
Musical/Rhythmic
Practice Book (page 55)
**
Santillana Spotlighton English3© SantillanaUSA
Name:
Date:
Jc^i )
Hedia^\]i dc 8dciZci
HX^ZcXZ
&#
Useful materials or substances are called
.
'#
A
is a solid substance found in nature, but it is neither a plant nor
an animal.
(#
When we talk about the characteristics of a mineral, we talk about its
.
)#
Solid materials made of minerals and found in nature are called
.
*#
The upper layers of earth where plants grow are called
.
&#
The
of a rock is the way it feels on the outside.
'#
The
is the layer or air that surrounds our planet.
(#
The components of our planetÕs atmosphere, such as oxygen, are known as
.
)#
A
is a substance, such as gasoline, that ignites into a fire.
6
Choose the correct word from the box to Þll in the blanks.
7
Choose the correct word from the box to Þll in the blanks.
properties
soils
resources
mineral
rocks
atmosphere
fuel
texture gases
8
Write three or four sentences explaining why rocks, gases, and soils are useful
resources.
Answers may vary.
mineral
properties
resources
rocks
soils
texture
atmosphere
gases
fuel
Standards
For a more complete and detailed description of
these and other national and state standards as
they relate to this unit of
Spotlight on English
,
please visit our Web site at
www.santillanausa.com.
Common Core State Standards
Reading: Informational Text
RI.3.1.
Ask and
answer questions to demonstrate understanding
of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the
basis for the answers.
RI.3.2.
Determine the main
idea of a text; recount the key details and explain
how they support the main idea.
Language
L.3.6.
Acquire and use accurately
grade appropriate general academic and domain
specific words and phrases, including those that
signal spatial and temporal relationships.
DECODING AND WORD RECOGNITION
63